
Surgical intervention is reserved for patients who fail non-operative treatment, and involves release of the cubital tunnel to improve the space available for the nerve. If symptoms persist or become more severe, a nerve conduction study may be used to evaluate the status of the nerve, and the location of nerve compression. Other causes of Guyon’s canal syndrome are anomalous muscles, abnormally thickened ligaments, and an anomalous course of the ulnar nerve 26.

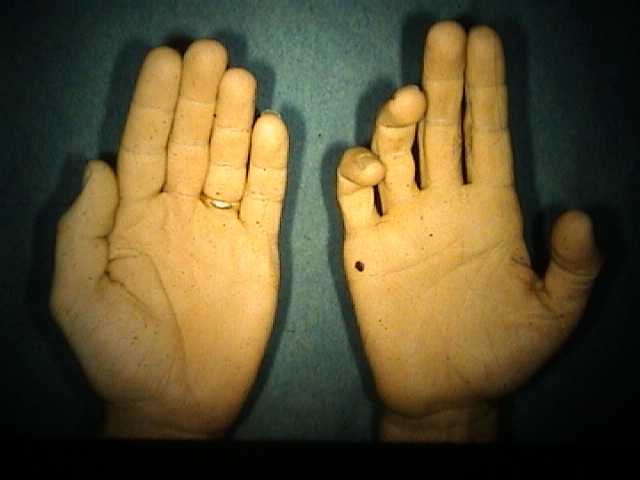
Anti-inflammatory medications may be used to help control the pain. A ganglion is one of the most common causes of Guyon’s canal syndrome, and other space-occupying lesions including tumorous conditions can cause ulnar nerve compression as well. The ulnar nerve goes round the back of the inner. Elbow pads or braces are used to prevent the elbow from bending during sleep at night. Ulnar nerve entrapment is caused when the surrounding tunnel between the forearm muscles becomes too tight. Initially, treatment for cubital tunnel syndrome focuses on avoiding activities that irritate the nerve. Typically these symptoms may be worse in the morning, as many patient sleep with bent elbows at night. The ring finger and small finger may feel as if they've "fallen asleep". Patients with cubital tunnel syndrome describe pain or numbness on the inside of arm and hand. Repeated pressure on the inside of the arm may cause similar symptoms as well.

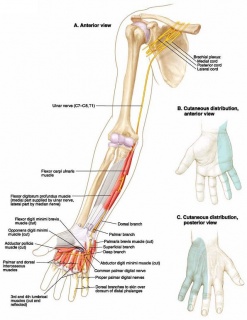
When the elbow bends, the nerve stretches around the medial epicondyle, and the space inside the cubital tunnel decreases. This tight space as is known as the cubital tunnel. Most commonly, this compression occurs at the level of the elbow, as the nerve runs in a tight space next to the bony bump (epicondyle) on the inside (medial aspect) of the arm. It can become compressed or irritated, which causes pain or numbness in the hand and arm. The ulnar nerve is one of the three main nerves that travels down the arm into the hand. During the day, an elbow pad may help protect against chronic irritation from hard surfaces.Cubital Tunnel Syndrome: Ulnar Nerve Compression at the Elbow Wearing a splint or foam elbow at night may help limit movement and reduce irritation.
Oral anti-inflammatory medications may ease pain and inflammation. The most effective treatment for cubital tunnel syndrome is ceasing any activity, such as bending, that has caused or aggravates the condition.ĭepending on the severity of your ulnar nerve issues, your doctor may recommend physical therapy, which can strengthen the ligaments and tendons in your elbow and hand. Cubital tunnel syndrome is compression or irritation of the ulnar nerve in a tunnel on the inside of the elbow (where your funny bone is). If left untreated, this condition can escalate to permanent injury to the arm or hand. That “funny bone” is actually the ulnar nerve where it crosses the elbow. The pain caused by this syndrome feels like the pain you feel when you hit the “funny bone” in your elbow. If this nerve is compressed as it passes through the elbow or wrist, the result is pain, numbness, muscle weakness, or tingling in your hands and arms.Ĭubital tunnel syndrome, like carpal tunnel syndrome, is a nerve compression condition. This nerve passes through the cubital tunnel, a tunnel of muscle, ligament, and bone located on the inside of the elbow. It transmits sensation and motor function to your lower arm and hand. The ulnar nerve starts in the side of your neck and ends in your fingers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
